Powers Apps vs. Power Automate: What's the difference?
Unlock the potential of Power Apps and Power Automate
Understand the difference between Power Apps and Power Automate
Power Apps is a low-code development platform for building custom business apps, while Power Automate, previously known as Microsoft Flow, automates workflows across various applications. Both are part of Microsoft's Power Platform low-code toolset. You can use Power Apps or Power Automate separately, but together they provide a comprehensive solution for organizations seeking to streamline and automate their processes.
Comparing their functionality
Unleash your creativity with Power Apps:
- Say goodbye to complex coding requirements as Power Apps allows users to craft custom business applications with ease.
- The intuitive platform features a drag-and-drop interface that accelerates app creation without compromising on functionality.
- Choose between canvas apps for flexible design options or model-driven apps for a more structured approach.
- Seamlessly integrate your apps with various data sources like SharePoint lists, Excel files, SQL databases, or external APIs.
- Leverage built-in formulas to execute intricate calculations and logic within your application.
Streamline operations with Power Automate:
- Formerly known as Microsoft Flow, this automation powerhouse simplifies repetitive tasks across multiple systems.
- Create automated workflows between applications such as Office 365, Dynamics 365, SharePoint Online, Salesforce CRM to eliminate manual efforts.
- Trigger flows based on specific events or conditions like email receipt or database record updates.
- Design flows using pre-built templates or build your own through a visual designer interface.
Key features in Power Apps
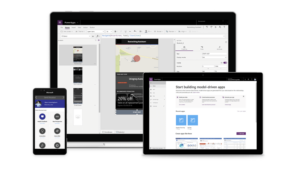
With Power Apps, you can probably create any app you might buy from another SaaS provider. Power Apps helps customers visualize data, integrate systems, and create mobile apps while backed by the security in their existing Microsoft environments.
- Intuitive interface: A standout feature of Power Apps is its user-friendly interface. The drag-and-drop functionality allows even non-technical users to design and build their apps easily, reducing reliance on IT departments or external developers.
- Tons of integration options: Power Apps seamlessly integrates with other Microsoft products such as SharePoint, Teams, Dynamics 365, and Azure services. Users can leverage existing data sources and workflows to create comprehensive solutions tailored to specific business needs.
- Mobile app development: Easily develop mobile applications across different devices and platforms with Power Apps. Whether you require an app for iOS, Android, or Windows devices, Power Apps provides the necessary tools for responsive mobile experiences.
- Data connectivity: Connect seamlessly with various data sources including Excel spreadsheets, SharePoint lists, SQL databases, Common Data Service (CDS), and more using Power Apps. Access real-time data from multiple systems within your organization directly through your app.
- Workflow automation: Simplify automating repetitive tasks with built-in workflow automation capabilities in Power Apps. Create automated workflows using triggers like button clicks or changes in data values without writing any code.
- Customization options: From designing visually appealing interfaces to adding custom logic using formulas or JavaScript functions - there are endless possibilities when it comes to customizing your Power app.
Key features in Power Automate
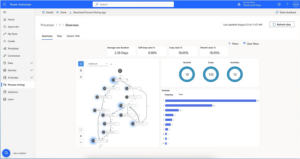
Previously known as Microsoft Flow, is a robust automation tool that lets users streamline workflows across various applications and services. Its user-friendly interface and extensive features make it a go-to choice for businesses looking to automate tasks efficiently and boost productivity.
- Seamless integration: Use connectors to popular platforms like SharePoint, Dynamics 365, Office 365, Teams, Azure services, and more. This integration allows users to connect different systems and data sources for smooth workflow automation.
- Visual workflow designer: The visual workflow designer in Power Automate offers an intuitive interface for creating automated workflows without the need for coding skills. Users can easily drag-and-drop actions onto the canvas to define their process flow.
- Pre-built templates: Power Automate provides a vast library of pre-built templates covering common business scenarios. These templates serve as starting points for quickly creating customized workflows.
- Custom connectors: Apart from built-in connectors for applications like Outlook or Excel Online, Power Automate enables users to create custom connectors using Azure Logic Apps or HTTP endpoints. This flexibility ensures seamless integration with any application or service not supported by default connectors.
- Data transformation: With its advanced data manipulation capabilities, Power Automate allows users to transform data from one format to another during automated workflows–crucial when dealing with disparate systems requiring specific data formats.
- Notifications and alerts: Users can set up notifications within their workflows through channels such as email notifications or push notifications on mobile devices via the Microsoft Teams app – keeping stakeholders informed about important updates in real-time.
- Security controls: To uphold data security standards, Power Automate offers robust security controls allowing users to define access permissions, encrypt sensitive data, and implement multi-factor authentication ensuring protection of their workflows and information handled.
A comprehensive comparison
Functionality:
- Power Apps: This platform allows you to craft custom business applications sans the need for coding. Its user-friendly interface facilitates app creation for web browsers, mobile devices, and offline usage.
- Power Automate: Conversely, Power Automate focuses on streamlining workflows across diverse systems and services through automated processes known as flows.
Integration:
- Power Apps: Both platforms seamlessly integrate with a range of Microsoft products like SharePoint, Teams, Dynamics 365, and Azure services
- Power Automate: While both offer integration capabilities with external systems via connectors or APIs, Power Automate boasts a broader array of pre-built connectors compared to Power Apps.
Development approach:
- Power Apps: With its visual development approach akin to Excel functions using drag-and-drop components and formulas, users can swiftly create functional apps without extensive coding knowledge in Power Apps.
- Power Automate: On the other hand, while some level of coding is feasible in both platforms (using expressions or JavaScript), developers may find more flexibility in extending functionalities within flows created in Power Automate.
Use cases:
- Power Apps: Building custom forms for data entry or approval processes, creating interactive dashboards for data visualization, developing mobile apps for field workers, etc.
- Power Automate: Automating approval processes, integrating data across different systems, sending notifications based on specific triggers, etc.
Strengths and weaknesses:
- Power Apps: The strength of Power Apps lies in its capacity to design visually appealing apps with an intuitive learning curve. It offers a comprehensive suite of controls, templates, and pre-built components that can be easily tailored.
- Power Automate: On the flip side, Power Automate shines due to its robust workflow automation capabilities enabling users to automate intricate business processes by linking various services together. However, it's worth noting that while both platforms are potent tools, they may have limitations when confronted with highly specialized or customized requirements.


